Spaying or neutering your dog is a significant decision that comes with various considerations, including the financial aspect. We’ll explore the costs associated with these procedures, the benefits of spaying or neutering your dog, the ideal timing for the procedure, options for veterinary clinics and low-cost clinics, as well as the risks involved in dog spaying and neutering.
Benefits of Spaying or Neutering Your Dog:
Spaying (for females) and neutering (for males) are crucial surgical procedures that offer numerous advantages for your furry friend:
- Population Control: One of the primary reasons for spaying or neutering dogs is to address pet overpopulation issues. By preventing unwanted litters, pet owners can play a vital role in reducing the number of homeless animals in shelters and communities.
- Behavioral Benefits: Spaying or neutering can significantly improve your dog’s behavior. It helps reduce undesirable behaviors such as roaming, aggression, marking territory, and the urge to mate. This leads to a calmer, more predictable, and easier-to-manage pet, fostering a stronger bond between the dog and their owner.
- Health Benefits: The health advantages of spaying or neutering are substantial. For females, spaying eliminates the risk of potentially life-threatening conditions such as uterine infections (pyometra) and significantly reduces the likelihood of mammary gland tumors and ovarian cancer. Neutering males reduces the risk of testicular cancer and may also lower the incidence of prostate problems.
- Longer Lifespan: Spayed or neutered dogs tend to live longer, healthier lives. By eliminating the risk of reproductive-related diseases and reducing the likelihood of certain cancers, these procedures contribute to an overall improved quality of life for your canine companion, allowing them to enjoy more years of happiness and companionship with their family.
Spaying or neutering your dog offers numerous benefits, ranging from population control and improved behavior to significant health advantages and an extended lifespan. It’s a responsible decision that not only benefits your pet but also contributes to the welfare of the entire community.
When to Spay or Neuter Your Dog:
Determining the optimal time for spaying or neutering your dog involves careful consideration of several factors, including breed, size, and overall health. While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer, veterinarians typically recommend the following guidelines:
- Age Range: Spaying or neutering is commonly performed between the ages of six months to one year. This timeframe allows for proper development while still providing the benefits of early sterilization. However, some smaller breeds may reach sexual maturity earlier, warranting earlier intervention.
- Breed Considerations: Larger breeds, such as Great Danes or Mastiffs, may benefit from delaying the procedure until they are fully mature, typically around 18 to 24 months. This allows for adequate growth and development of their skeletal structure, potentially reducing the risk of orthopedic issues later in life.
- Health Assessment: Before scheduling the surgery, it’s essential for your veterinarian to conduct a thorough health evaluation of your dog. Dogs should be in good overall health and free from any underlying medical conditions that could complicate the procedure.
- Behavioral Considerations: Some behavioral factors, such as aggression or marking behaviors, may influence the timing of the procedure. In such cases, consulting with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can help determine the most appropriate timing for spaying or neutering.
Ultimately, the decision on when to spay or neuter your dog should be made in consultation with your veterinarian, taking into account your dog’s individual needs and circumstances. Early intervention can provide numerous benefits, but it’s essential to weigh the potential risks and benefits for your specific pet.
Veterinary Hospitals vs. Low-Cost Clinics:
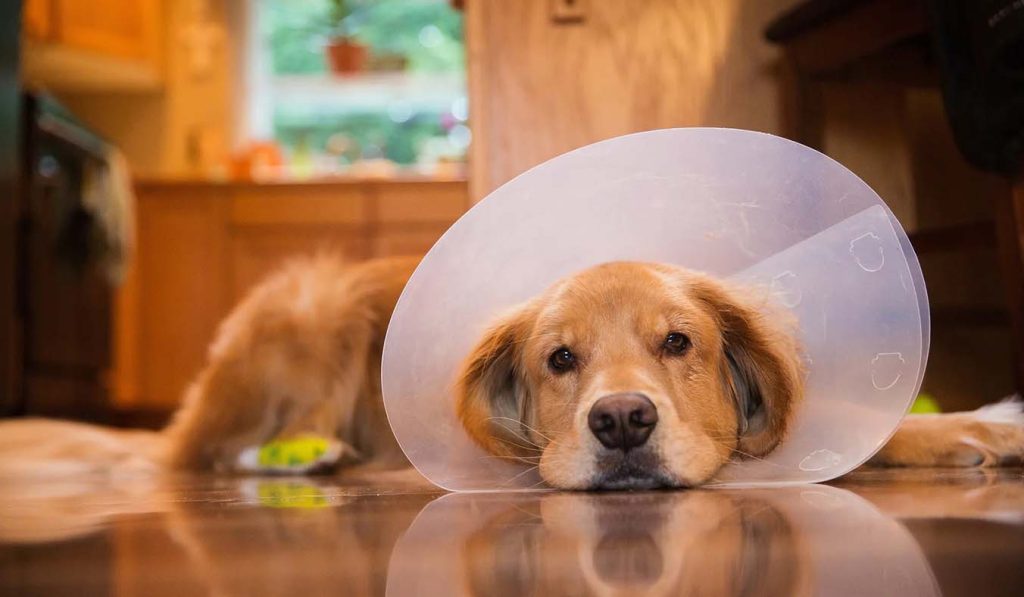

When considering where to spay or neuter your dog, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of veterinary hospitals versus low-cost clinics:
Veterinary Hospitals:
- Comprehensive Care: Veterinary hospitals offer comprehensive medical care, including pre-surgical examinations, anesthesia monitoring, and post-operative monitoring.
- Experienced Staff: Veterinarians and veterinary technicians in hospitals are highly trained and experienced in performing spaying and neutering surgeries, ensuring the procedure is conducted safely and efficiently.
- Advanced Facilities: Veterinary hospitals often have access to advanced medical equipment and facilities, which may be beneficial in cases where additional diagnostics or treatments are required.
- Personalized Care: Your dog receives individualized attention and care throughout the entire process, from pre-surgical assessments to post-operative recovery.
Low-Cost Clinics:
- Affordability: Low-cost clinics typically offer spaying and neutering services at a fraction of the cost compared to veterinary hospitals, making it more accessible for pet owners on a budget.
- Community Outreach: Many low-cost clinics are associated with animal welfare organizations or non-profit groups, aiming to provide affordable spay/neuter services to reduce pet overpopulation and homelessness.
- Convenience: Low-cost clinics may offer flexible scheduling options and convenient locations, making it easier for pet owners to access essential veterinary care for their dogs.
- Basic Services: While low-cost clinics may not provide the same level of comprehensive care as veterinary hospitals, they focus primarily on spaying and neutering procedures, ensuring affordability without compromising on the quality of the surgery.
Ultimately, the decision between a veterinary hospital and a low-cost clinic depends on your budget, the specific needs of your dog, and your preferences regarding the level of care and services provided. It’s essential to research and evaluate both options carefully to ensure the best possible outcome for your furry friend.
Risks Associated with Dog Spaying and Neutering:
While spaying and neutering are common and generally safe procedures, they do carry some risks, including:
- Anesthesia Risks: Like any surgical procedure, spaying or neutering requires anesthesia, which carries a small risk of complications such as allergic reactions or adverse effects on the heart and respiratory system.
- Surgical Complications: Although rare, complications such as bleeding, infection, or poor wound healing can occur following spaying or neutering surgeries.
- Potential Long-Term Health Effects: Some studies suggest that early spaying or neutering may be associated with an increased risk of certain health issues, such as orthopedic problems or certain cancers. However, more research is needed to fully understand these associations.
- Hormonal Changes: Spaying or neutering removes the reproductive organs, leading to hormonal changes that may affect metabolism, behavior, and overall health. While these changes are usually beneficial, they can sometimes result in unexpected side effects.
- Weight Gain: Dogs may be more prone to weight gain after spaying or neutering due to changes in metabolism and hormone levels. Proper diet and exercise can help mitigate this risk.
- Urinary Incontinence: Female dogs, especially larger breeds, may experience urinary incontinence after spaying, although this is relatively uncommon and can often be managed with medication.
- Behavioral Changes: Spaying or neutering may influence certain behaviors such as aggression, fearfulness, or anxiety. However, these changes are typically positive and contribute to a more well-behaved and balanced pet.
It’s essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of spaying or neutering with your veterinarian to make an informed decision that is best for your dog’s health and well-being. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper post-operative care can help minimize the likelihood of complications and ensure a smooth recovery process.
Spaying or neutering your dog is an essential aspect of responsible pet ownership that offers numerous benefits for both your furry companion and the community. While the cost of these procedures may vary, the long-term advantages far outweigh the initial investment. It’s essential to discuss the timing and specifics of spaying or neutering with your veterinarian to ensure the best possible outcome for your dog’s health and well-being.


.jpg)
